What is Encryption?
Encryption is the process of transforming a message into a secret code. Imagine you have a note that you only want your friend to read. You change the words of the note into a code that looks like random letters and numbers. Now, even if someone else finds your note, they won’t understand it because it’s in code.
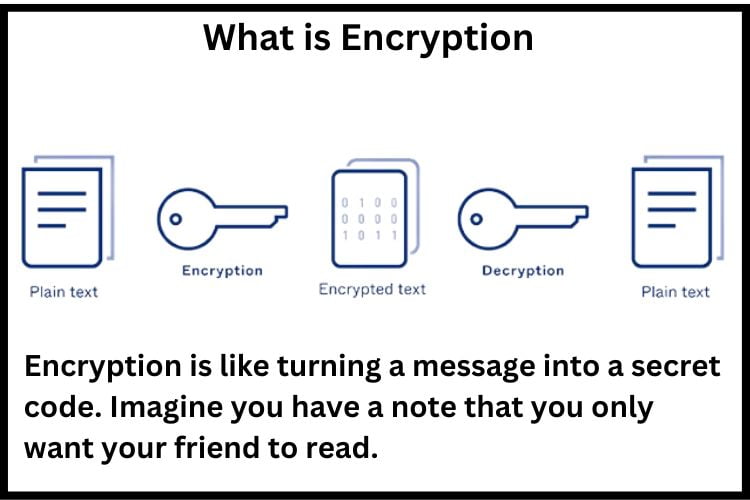
Your friend, who knows how to turn the code back into the original message (we call this decoding or decrypting), can read it. Just like the note, encryption changes your private information on the internet into a code. Only the people or services that have the key can change it back and understand it. This keeps your information safe from others who are not supposed to see it.
Why Do We Need Encryption?
We need encryption because it’s like a lock that keeps our private information safe online. When we shop, chat, or share anything on the internet, we don’t want strangers to see our details. Encryption helps by turning our information into a secret code that only people we trust can understand.
Without encryption, it would be like sending postcards that anyone could read. With encryption, it’s like sending locked safes that only the recipient has the key to open. This keeps our messages, shopping details, and personal information safe from hackers.
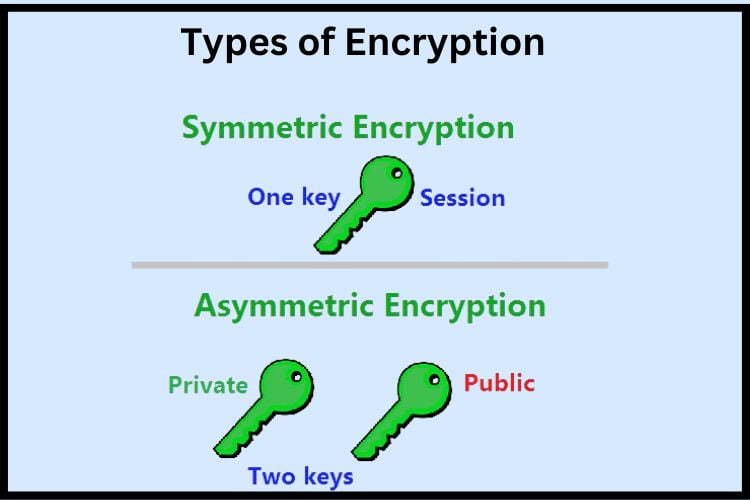
Types of Encryption
- Symmetric Encryption: Here, the same key is used to encrypt and decrypt data. It’s like a locked box with a single key. While it’s faster than other types, if the key is stolen, anyone can access your data.
2. Asymmetric Encryption: This type uses two keys – a public one for encryption and a private one for decryption. Think of it as a mailbox where anyone can drop a letter (encrypt data), but only you have the key to open it (decrypt).
3. End-to-End Encryption: This ensures that only you and the recipient can read the messages. Even the service provider can’t access your data. It’s like sending a letter in a language that only you and your friend understand.
Advantages:
- Privacy: Encryption keeps your personal information safe from unauthorized access.
2. Security: It protects your data from cyber threats like hacking and identity theft.
3. Trust: Using encryption can build trust with your customers or friends, knowing that their data is protected.
5. Secure Online Transactions: When you shop or bank online, encryption protects your financial information, keeping your transactions safe.
Disadvantages:
- Complexity: Implementing and managing encryption can be complex and requires technical expertise.
2. Performance: Encryption can slow down system performance due to the extra processing required.
3. Recovery: If you lose your encryption keys, you might not be able to access your own data.
5. Cost: While many encryption tools are free, some advanced options can be costly, particularly for businesses that need to encrypt a lot of data.
Conclusion
Encryption acts as a strong lock for your online data, keeping it safe from hackers. It turns your private information into a secret code, protecting your online activities. Using a Shared Proxy adds a basic level of anonymity, like joining a crowd. For more security, a Private Proxy gives you your own hidden space online, offering stronger protection.
Proxiesforrent provides both types of proxies, helping you choose how hidden you want to be. They work with encryption to make your online presence much safer.
Frequently Asked Question
While encryption is powerful, it’s just one piece of the puzzle. You should also use strong passwords, update your software, and be careful about what you download or click on.
Check the URL. If it starts with “HTTPS” and you see a padlock icon, your connection to the site is encrypted.
Common encryption methods include SSL/TLS for websites, WPA2 for Wi-Fi networks, and end-to-end encryption for messaging apps and email services. It’s important to choose services and products that use strong encryption standards.
Yes, using email encryption ensures that your messages are read only by the intended recipients. Encrypted emails are converted into a secure format that cannot be read by anyone who intercepts them during transmission or gains unauthorized access to the recipient’s inbox.